
A network address is any logical or physical address that uniquely distinguishes a network node or device over a computer or telecommunications network. It is a numeric/symbolic number or address that is assigned to any device that seeks access to or is part of a network.
EXAMPLE OF NUMERIC ADDRESS:
IP VERSIONS :
IPv4 :
Network switch port management tool helps network engineers identify the switch port to which a device is connected and thus eliminates the need of manually tracing the network cables. The tool discovers the devices plugged into each port of a specified switch. The tool is useful for system and network engineers to gain visibility into the IP, MAC, VLAN, status and availability of ports. Since this is a real-time discovery, the administrators can also view the operational status and speed of each port.
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet.
CLASSES OF IP ADDRESS :
IP Address Classes: IP addressing supports three different commercial address classes; Class A, Class B, and Class C. In a class A address, the first octet is the network portion, so the class A address of, 10.1.25.1, has a major network address of 10. Octets 2, 3, and 4 (the next 24 bits) are for the hosts
HOW TO SET IP ADDRESS
To set a static IP on your Windows computer:
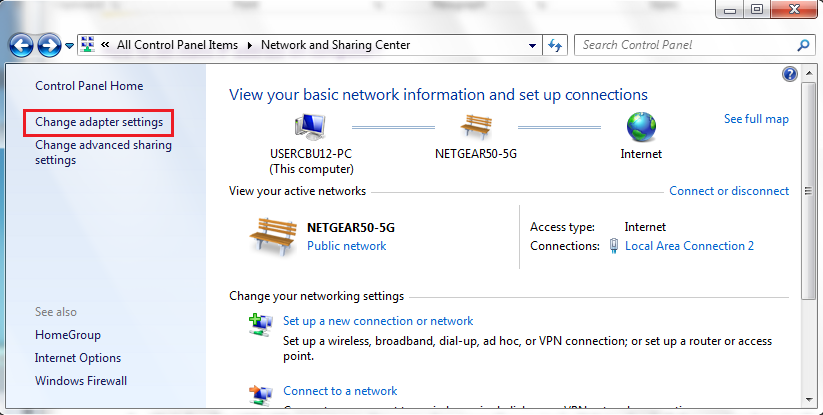
- Click Start Menu > Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center. (For Windows 8 and higher, search for and open Control Panel and select Network And Internet).
- Click Change adapter settings.
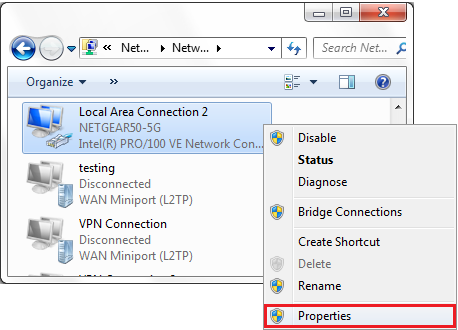
- Right-click on Local Area Connection and click on Properties.
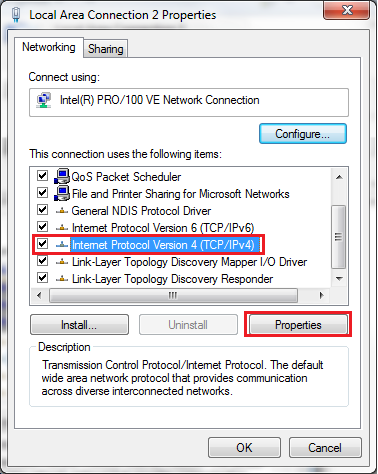
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click on Properties.
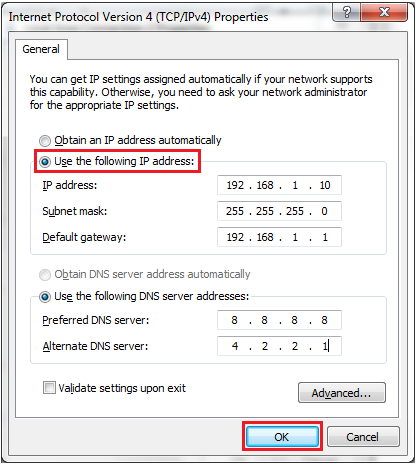
- Select "Use the following IP address" and enter the IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway. and DNS server. Click OK and close the Local Area Connection propertieswindow.
Source: Google



